What is the pH of hair?
A study with Italian trichologists showed that the vast majority of anti-dandruff shampoos have a pH above the skin’s physiological pH, which lies between 4.5 and 5.5.
In the case of medicated and conventional shampoos, the differences were small, but the majority of shampoos had a pH above the physiological pH.
In this study, only professional shampoos from hair salons in Italy had a physiological pH or lower.
The study involved over 120 different shampoos, with pH values ranging from 3.5 to 9.0.
The study was conducted using litmus paper and a pH limit of 5.5 was determined, which shampoos had lower pH values and which were higher.
Why is this aspect so intriguing? Because the pH values of skin and hair are different, we often find that a shampoo that works on the length of our hair doesn’t necessarily work on the scalp, and vice versa.
What’s more, maintaining the right pH level contributes to a healthy scalp and healthy hair.
The scalp, like the skin on the face and body, has a pH of between 4.5 and 5.5, which helps preserve the skin’s microbiome.
In the case of the scalp, this is important, as our physiological bacteria are able to combat pathogenic microbial flora.
It’s worth noting that, for example, dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis are exacerbated by bacteria and yeast, most commonly Pityrosporum ovale.
However, the type of microorganisms colonized is not only important in the case of dandruff or psoriasis, the pathogenic flora hinders the healing of scalp inflammation, pimples, redness and itching, and the regeneration of the epidermis.
Using shampoos with a higher pH than that of the scalp ensures stronger cleansing of the scalp, i.e. not only eliminates excess sebum, but also helps break down the epidermal hydrolipid barrier.
Thanks to this action, hair is better rebounded at the roots and stay fresher longer, at least during the first few applications of shampoo.

The skin’s hydrolipidic barrier
When the hydrolipidic barrier is broken on the scalp, the effect is the same as on the rest of the body: the skin begins to activate the sebaceous glands to not only rebuild the hydrolipidic barrier, but also to create a physical barrier to protect the skin from the damaging effects of overly aggressive shampoos.
The use of increasingly powerful washing cosmetics leads to a simultaneous increase in seborrhea, which in extreme cases makes the hair so greasy that it has to be washed every day.
At the same time, there’s the problem of dandruff, which only disappears with the use of very powerful shampoos with a pH well above the physiological value.
Attempts to switch back to milder shampoos usually fail, with a serious relapse of dandruff and a forced return to aggressive cleansing shampoos, which progressively weaken hair and hair follicles.
The high pH has a keratolytic effect, exfoliating epidermal cells.
Consequently, by using shampoos, we get rid of frizz and dry cuticles.
This effect is similar to, but stronger than, that of acids, as our skin and hair tolerate acids better than bases.
As long as we use a strong cleansing shampoo, it can usually cope with the flaking of the epidermis resulting from dry scalp, which is at the same time intensified by these shampoos.
Shampoo against dandruff relapse
When it leaves such a shampoo, the skin tries to regenerate itself, to rebuild the epidermis and the hydrolipid barrier, but it has to get used to the work of its glands under new conditions, which is a milder shampoo.
This is why we generally see an increase in the oil content of the scalp after switching to a milder shampoo.
At the same time, the dandruff problem reappears: stopping using a shampoo which, thanks to the slightly alkaline pH most often found in anti-dandruff shampoos, according to the above-mentioned study, has exfoliated the epidermal surface, causes dandruff to reappear.
The skin needs time to rebuild the epidermal layer in a watertight manner and to improve its hydration.
Once the skin has regained its physiological functions, the above-mentioned problems, such as seborrhea and dandruff, disappear. Of course, this is a problem caused by inappropriate care; dandruff or seborrhea resulting from illness or medication should be discussed with your doctor.
So, when you change your shampoo for a gentler one, give yourself some time. Generally speaking, problems disappear after 2 or 3 weeks.

Hair has a lower pH than skin
Our hair, on the other hand, has completely different properties to our scalp.
It’s dead, not innervated, and so doesn’t transmit to the body the information that defense mechanisms need to be activated. In the case of long hair, it can’t be covered by the protective barrier of sebum secreted by the scalp’s sebaceous glands.
As a result, they are more prone to moisture loss and become fragile in the event of excessive dryness.
It’s difficult to measure the pH of hair, as it contains a small amount of water.
This value can be roughly calculated from the isoelectric point, and on this basis, it is estimated that the pH of hair is around 3.68, which is also presented by Italian trichologists.
Hair has a lower pH than skin, so the effectiveness of a vinegar rinse should come as no surprise.
The use of cosmetics or preparations with an acidic pH closes hair cuticles, making them smoother and shinier.
The same applies to high pH products such as anti-dandruff shampoos.
Black soap pulls the hair’s cuticles apart, leaving it rough and frizzy.
The scales that adhere tightly to the core form a mechanical barrier, while the peripheral scales expose the hair to damage and breakage.
Consequently, aggressive shampoo washes used systematically over a long period (e.g. several years) considerably weaken the hair, its roots and the scalp itself.
What is the link between pH hydrogen potential and hair care?
Let’s go back to school for some chemistry lessons.
The pH hydrogen potential scale determines the degree of acidity and alkalinity of any aqueous solution.
It was introduced into common usage in 1909 by Danish chemist Søren Peder Lauritz Sørensen to simplify and facilitate calculations.
He defined pH as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration.
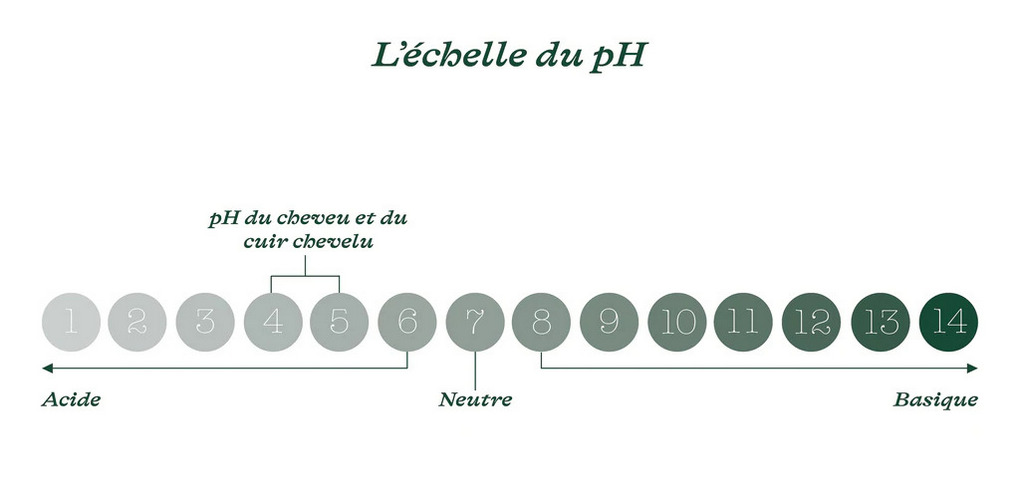
It assumes a range from 0 to 14, with neutral solutions having a pH of 7.
Below this range, solutions are acidic; the lower the value, the more acidic they are. In other words, “0” corresponds to a solution that is as acidic as possible, such as hydrochloric acid.
The higher the value, the more alkaline the product, such as sodium hydroxide, which has a pH of 14.
Everything that contains water has its own pH value.
This applies to cosmetics as well as skin and hair care products.
That’s why it’s so important to choose skin care products whose pH is adapted to our own pH.
The natural pH of the skin, and therefore of the scalp, is between 4.5 and 6.0, while hair has a lower pH of around 3.6.
Fortunately, the difference is not great and, more importantly, is on the same side of the scale, i.e. slightly acidic.
The same shampoo can therefore be used, ideally with a pH of approximately 5 for both scalp and hair.
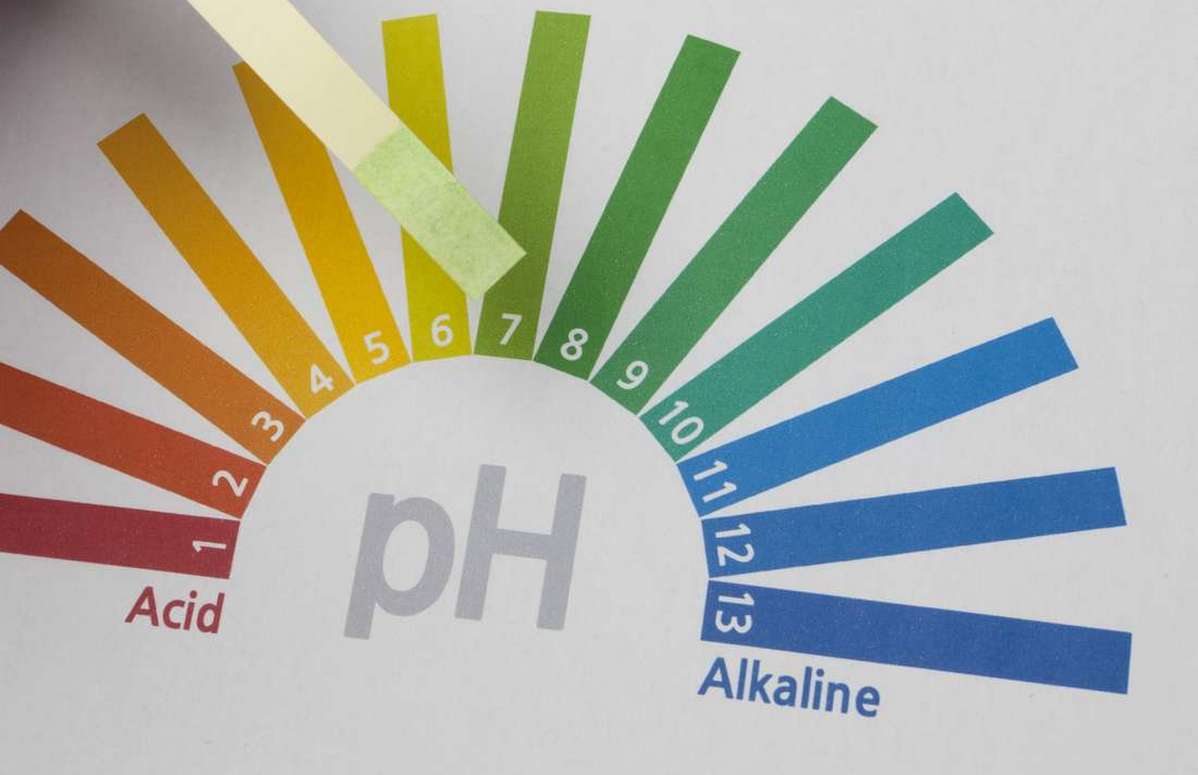

What happens if we use products with an acidic pH below 7?
They also have their advantages, as long as you don’t overuse them.
Grandmothers in Quebec used to rinse their hair in vinegar to make it shine.
In fact, acidity restores shine, makes hair feel fresher, closes cuticles, which is important for color-treated hair, and facilitates the removal of residual impurities.
Acidity creates a hostile environment for unwanted bacteria.
Negative effects include dry hair and skin
Alkaline, on the other hand, opens the hair cuticle, making it easier for nutrients or dyes to penetrate the hair.
This is why colorants have a higher hydrogen potential, and the conditioner used after coloring must be acidic.
But beware: too frequent use of the acid-base combination during shampooing can damage the hair shaft and prevent cuticles from closing.
Also read: finasteride side effects in women and men
A disturbance in the hydrogen potential level of the scalp can lead to a number of problems:
- Dandruff or seborrhea, scalp irritation, itching and discomfort, dry, dull, porous and unruly hair.
“One of my biggest dreams is that my company will be able to change the course of one family’s life, one child at a time by giving back to the community.”







